Images by Computer
- Pixel is the smallest unit of image information which can be controlled by a computer
- Digital Image is a sequence of pixels in a rectangle disposition
- Image Dimension is measured in Width x Height pixels, and it is common practice to specify Width first, ie: 1024×768 pixels
- Colour System: each pixel has got a colour from a maximum range of any of these Colour Systems:
- BLACK and WHITE: uses 2 colours = 21 = 1 bit
- SCALE of GRAYS: uses 256 greys = 28 = 8 bits = 1 Byte
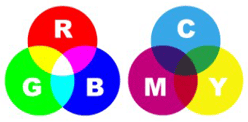
- RGB: uses 256 colours per channel (Red, Green, Blue) = 28 x 3 = 24 bits = 3 Bytes
- CMYK: uses 256 colours per channel (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, blacK) 28 x 4 = 32 bits = 4 Bytes
- Image Resolution is the number of pixels per physical size, the most common is DPI (dot per inch)
- Colour Profile define a colour mapping of a particular device, and has to be carried on during all the image manipulation process to preserve consistence in colour representation.
Images for Printing
- Printers use ink, so the colour system is CMYK
- Resolution is only important for printing, and a good resolution for printing is 300 dpi
- Colour Profile: If your image for printing does not have a Colour Profile, use AdobeRGB
Images for Web
- Screens use light, so the colour system is RGB
- Resolution is not relevant for web images
- Colour Profile: Use always sRGB (do not embed it when saving)
- Save photos in JPG in progressive mode and graphics in PNG
Images for Web »
Image Formats
|
PSD |
JPG |
PNG |
GIF |
| Compression |
Lossless data compression (no losing image quality) |
Lossy data compression (losing image quality) |
Lossless data compression (no losing image quality) |
Lossless data compression (no losing image quality) |
| Colour System |
Any colour system |
Any colour system |
PNG-24: Any colour system |
PNG-8: 256 colours |
Only 256 colours |
| Transparencies |
Yes |
Not allowed |
PNG-24: Yes, better than GIF |
PNG-8: Yes |
Yes |
| Animation |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
| Use as Master |
Yes, Recommended |
No, as when re-open and re-save we lose quality due to degradation in Lossy data compression |
PNG-24: Yes |
PNG-8: No, as we have only 256 colours now |
No, as we have only 256 colours now |
| Web Format |
No |
Yes, Recommended for photos (many colours) + reducing file size (compromise between compression and file size) |
PNG-24: Yes, Recommended for photos (many colours) |
PNG-8: Yes, Recommended for graphic and logos (few colours) |
Yes, Recommended for graphic and logos (few colours) |
Manipulating Images for Web: Use Photoshop
- Colour System: in Photoshop: Image > Mode
- If image is in full colour, verify that the image mode is RGB (as CMYK is for printing)
- If image is in gray scale, verify that the image mode is GRAY SCALE (file size smaller than RGB)
- Image Resolution: This is not relevant for web
- Colour Profile: Use always sRGB
- Resampling pixel dimensions: In Photoshop: Image > Image Size
- Downsampling: Reduce width and height pixels > Allowed > But you lose those pixels forever
- Upsampling: Increase width and height pixels > Forbidden > Blur image, as new pixels are created
- Save Image: As PhotoShop PSD or PNG-24 >>> This is your IMAGE MASTER
never as JPG (as we lose quality) or GIF/PNG-8 (as we loose colours)
- Save Image for Web: As JPG or PNG >>> This is your IMAGE FOR WEB
If it is a photo use JPG progressive or If it is a graphic use PNG
- Next time to need to make any modifications to your web images take the IMAGE MASTER, make your modifications in PhotoShop, save your new IMAGE FOR WEB and save again YOUR MASTER
Images Utilities
A very nice guide. I will definitely follow these tips. Thank you for sharing such detailed article. I am learning a lot from you.
Thank you for your feedback… for web remember: photo images in JPG, never in PNG